Never miss an offer or update. You can unsubscribe at any time.
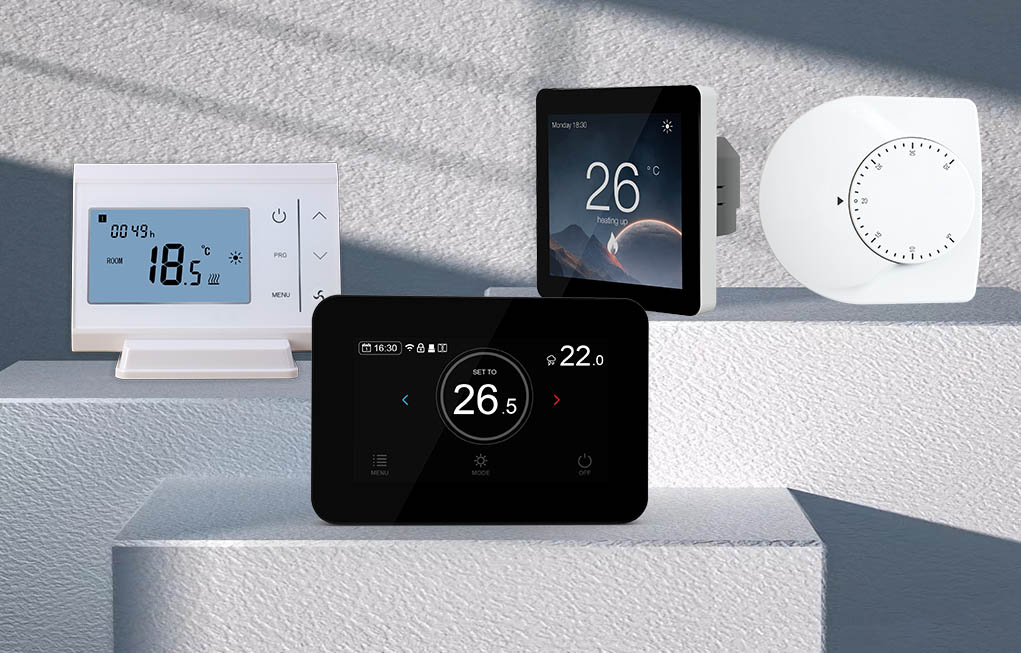 Types of thermostat
Types of thermostat
 Address:No.6 of Tong'an Industrial Park, Meixi Rd,Tong'an District, Xiamen China 361100
Address:No.6 of Tong'an Industrial Park, Meixi Rd,Tong'an District, Xiamen China 361100 Phone:+86 0592 6155792
Phone:+86 0592 6155792 Email:info@etopcontrols.com
Email:info@etopcontrols.comNever miss an offer or update. You can unsubscribe at any time.

